Kubeflow 1.8: Kubernetes MLOps delivered via Python workflows
Kubeflow v1.8’s powerful workflows uniquely deliver Kubernetes-native MLOps, which dramatically reduce yaml wrangling. ML pipelines are now constructed as modular components, enabling easily chainable and reusable ML workflows. The new Katib SDK reduces manual configuration and simplifies the delivery of your tuned model. v1.8 also introduces the PVC Viewer for easier persistent storage management eliminating the need for Kubernetes CLI storage commands.
Kubeflow 1.8 adds ARM processor support which simplifies adoption for Apple Silicon users and IoT servers. 1.8 delivers updated Tensorflow, PyTorch, Cuda notebook image examples with a detangled makefile process. Kubeflow’s performance and security are improved via significant upgrades to the underlying components and packages.
Selected and Highlighted deliveries
Kubeflow Pipelines
Kubeflow 1.8 includes KFP 2.0.3 and KFP SDK 2.4.0. The KFP Python SDK 2.4.0 release contains features present that were previewed in the v2 namespace with now full official support along with considerable additional functionality. A selection of these features include:
- An improved and unified Python-based authoring experience for components and pipelines
- Support for using pipelines as components (pipeline in pipeline)
- Various additional configurations for tasks
- Compilation to an Argo-independent pipeline definition that enables pipelines to be compiled once and run anywhere
- An improved KFP CLI
- Refreshed user documentation and reference documentation
This pipeline release is focused on cross-platform portability, features such as reading and writing to a Kubernetes PVC has been moved into the extension package kfp-kubernetes, more information can be found at the platform specific features page on the Kubeflow Website.
Additionally the project kfp-tekton which allows users to run pipelines with a Tekton backend, is also updated version 2.0.3 and the sdk will compile to the same pipeline spec, sdk users can use the same pipeline definition to run on both Argo and Tekton backends.
Katib
The updated Katib pythonic SDK in Kubeflow v1.8 helps developers to improve model quality by simplifying the configuration and tracking of model and environmental parameters. In this release we are happy to announce new KatibConfig API (#2176) along with multiple commits improving the experience in the UI and bug fixes in the SDK. A selection of these features and bug fixes include:
- Upgrade Tensorflow version to v2.13.0 (#2216)
- Start waiting for certs to be ready before sending data to channel (#2215)
- Remove a katib-webhook-cert Secret from components (#2214)
More information on the release can be found in the release notes
Training Operator
Many model developers are experiencing challenges with GPU utilization, especially with large language models. The new training operator functionality provides efficient configuration, utilization and scaling for training. v1.8 improves support for gang schedulers such as volcano, scheduler-plugins and koord-schedule (#1747). Additionally the implementation of suspend semantics allows the external controller to delete or not create Pods depending on the state of the flag (#1859). V1.8 also includes workflow updates and bug fixes that make model training more straightforward to use. A selection of these features and bug fixes include:
- Make scheduler-plugins the default gang scheduler. (#1747)
- Auto-generate RBAC manifests by the controller-gen (#1815)
- Set correct env variables for PytorchJob to support torchrun, allowing to support different distributed training launch methods (#1840)
- Add default Intel MPI env variables to MPIJob (#1804)
- Fully consolidate tfjob-operator to training-operator (#1850)
More information on the release can be found in the release notes
KServe
Kubeflow v1.8 introduces KServe 0.11. In this release, we’ve introduced Large Language Model (LLM) runtimes, made enhancements to the KServe control plane, and updated the Python SDK with revised support for the Open Inference Protocol, as well as improved dependency management using poetry. A selection of these features and bug fixes include:
- TorchServe 0.8.0 for LLM support (#2980)
- Implement v2/open inference endpoints for kserve python runtimes (2655)
- Adding an end-to-end example for deploying a large language model on KServe (2836)
More information on the KServe 0.11 release can be found in the release notes
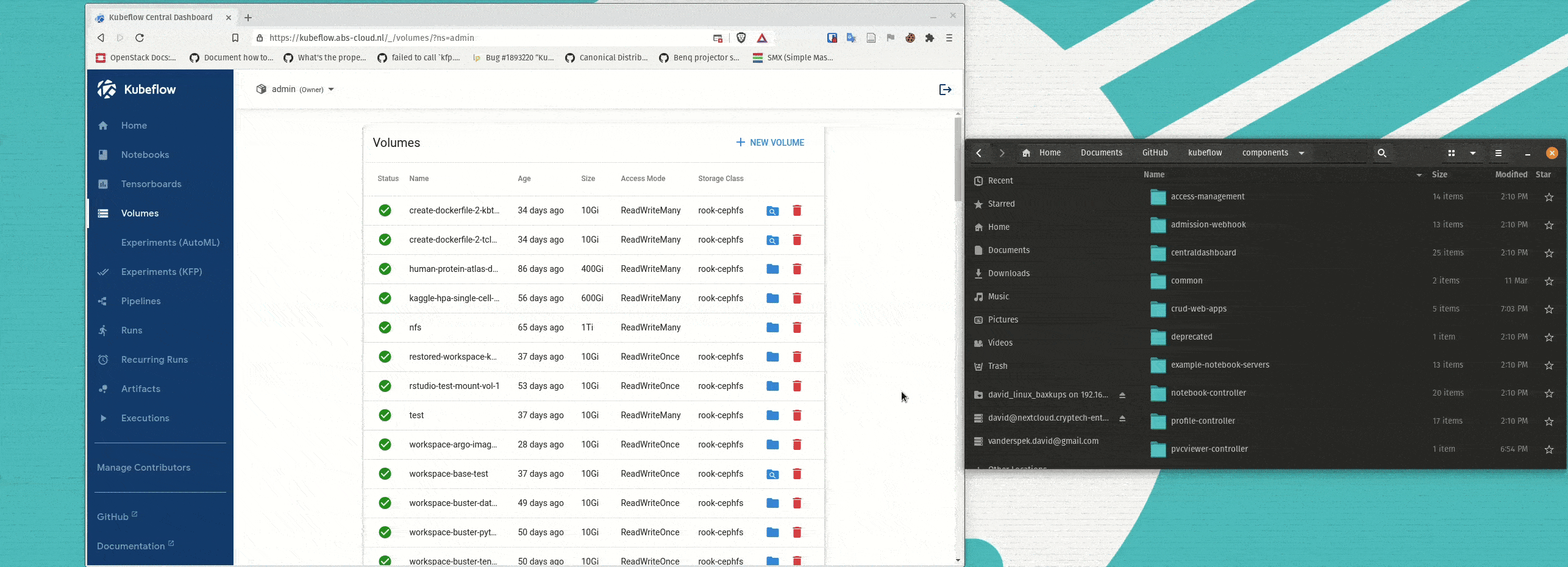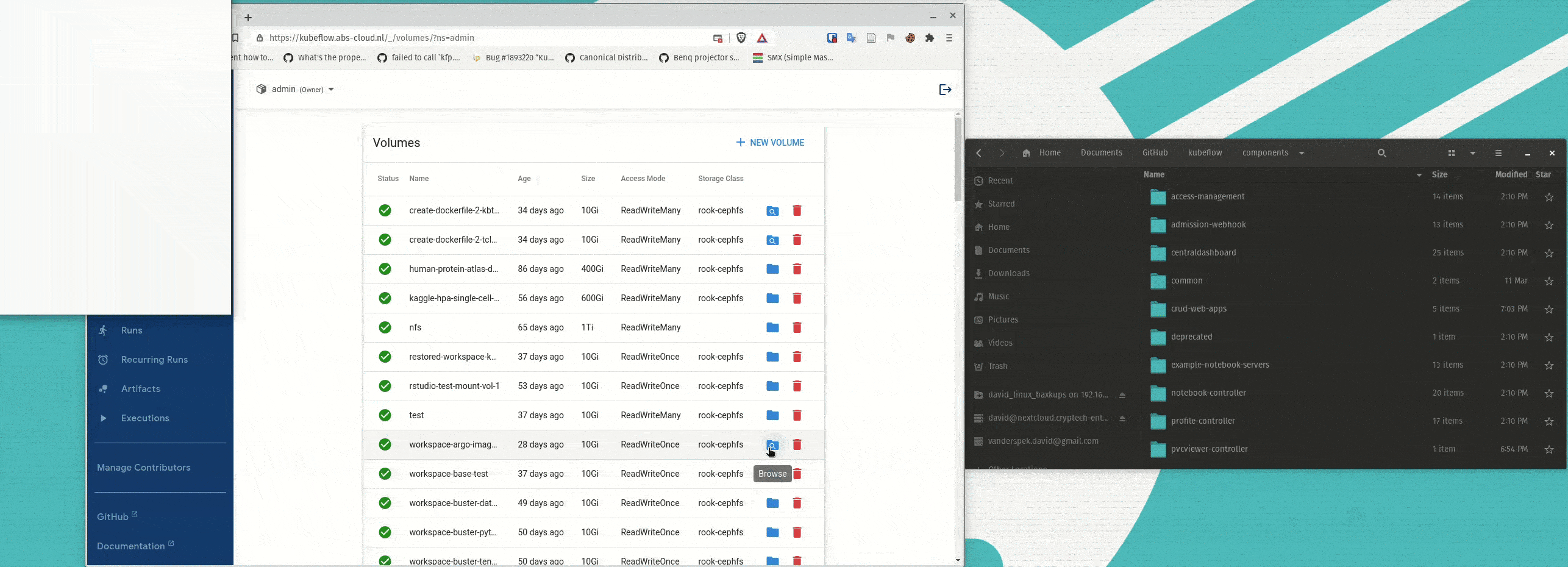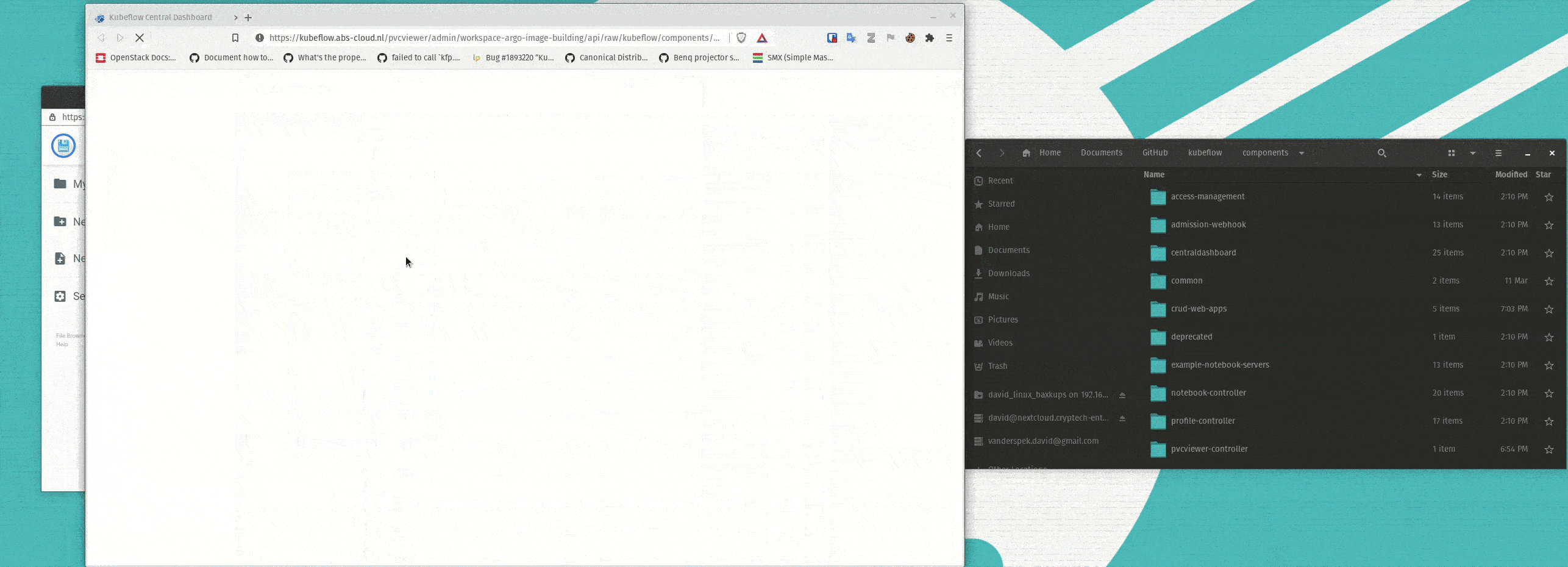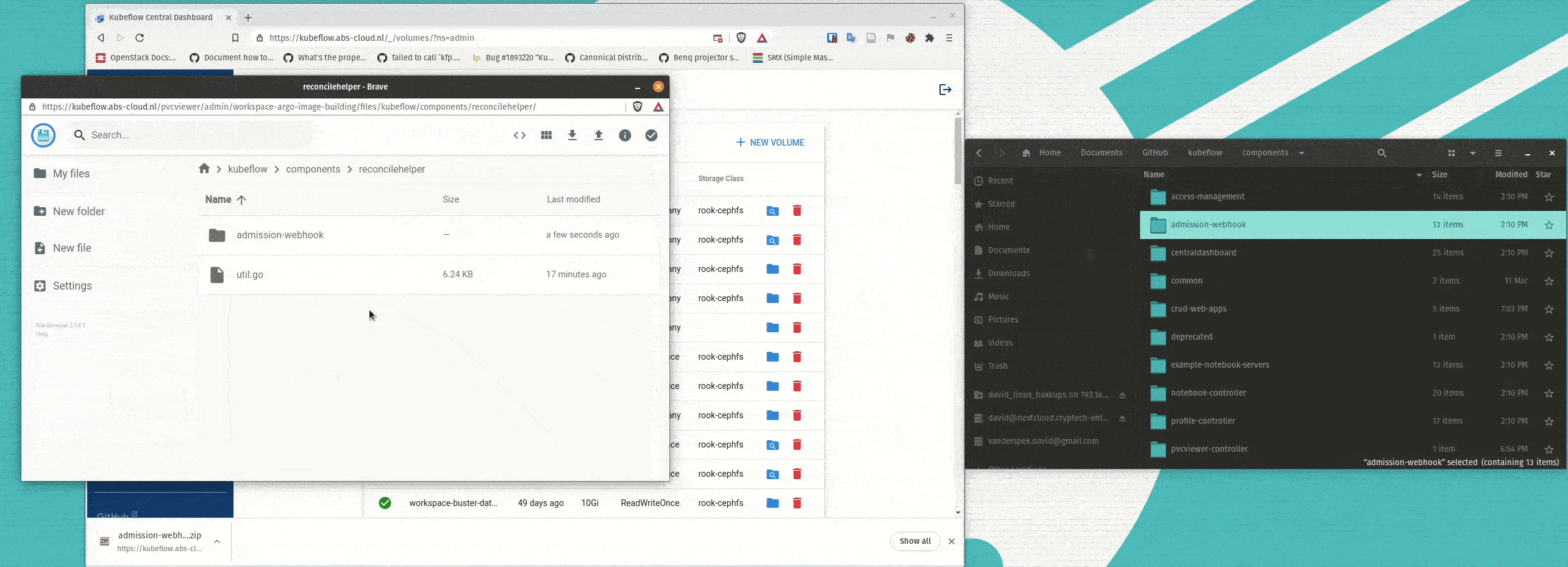
Simplifying Storage for ML Workflows
Kubeflow’s web apps enhancements expose valuable information to data scientists, which simplifies advanced workflows. For example, Kubernetes storage management, especially for persistent volumes, is critical for rapid data science iteration but can require complex, manual configuration. The newly introduced PVC Viewer makes storage management easy for end users and eliminates the need to learn low-level CLI commands. Users can click and drag to add/remove files and file directories from persistent volumes. The volumes can easily be attached to MLOps objects, like notebooks, which makes experimenting with different data sets faster.
Support for ARM Machines
Kubeflow 1.8 brings forward a significant upgrade (#7343) by officially introducing support for ARM architectures. This move ensures that developers can leverage Kubeflow’s powerful machine learning capabilities on a wider variety of devices and platforms, including the Apple Silicon and a multitude of IoT devices. This expansion highlights Kubeflow’s adaptability, ensuring seamless machine learning workflows across various hardware architectures.
Security - Rootless Kubeflow Updates and Fixes
In our ongoing commitment to bolstering security, version 1.8 brings both vital security fixes and innovative features. A notable endeavor by the Security Team has been the development of features that lay the groundwork for a rootless Kubeflow #2455 in the future. v1.8 offers users the flexibility to run Kubeflow either with the optional istio-cni or without it. A selection of these features and bug fixes include:
- Fix performance issue within a mysql request that could cause a denial of service (#9680)
- Fix issue on which Profile controller and KFAM allow unauthenticated in-cluster traffic(#7032)
- Adding oauth2-proxy as optional alternative to oidc-authservice (#2409)
Future versions will continue to refine this rootless functionality, along with plans to make istio-cni the default option along with istio ambient mesh and incorporating Pod Security Standards. Please join the Security Team
Notebooks
Kubeflow Notebook 1.8 brings many enhancements to the notebook container images.
This chart shows how the official images are now related to each other
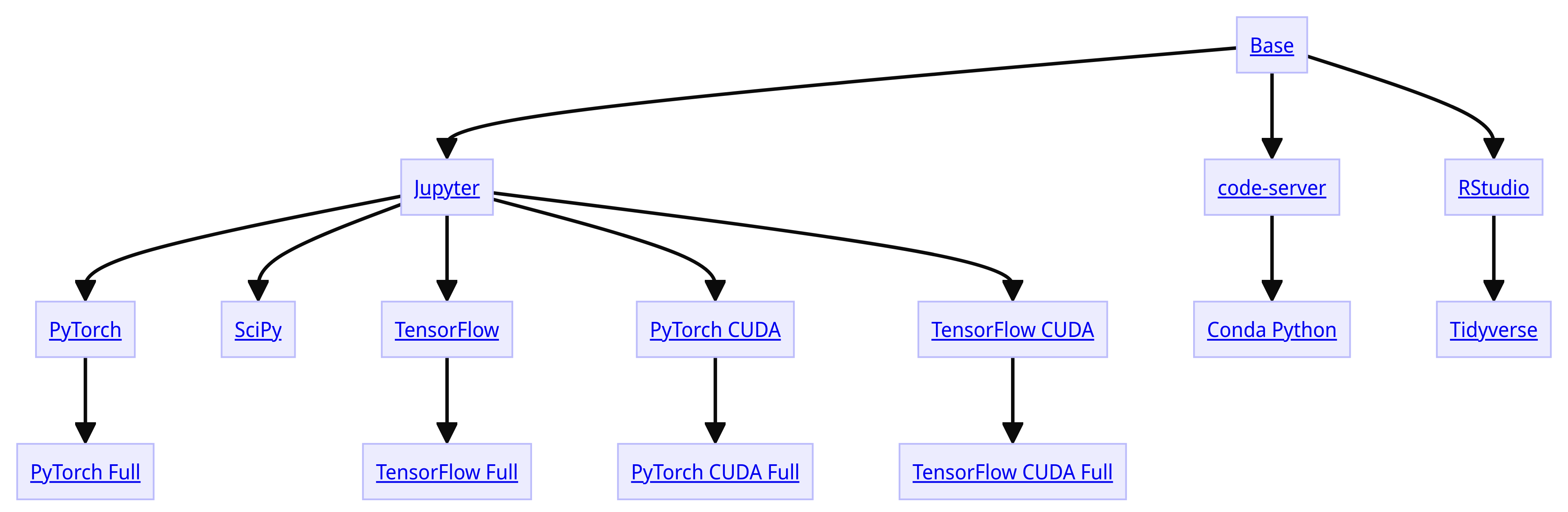
Of special note is that all notebook images (except the CUDA ones) are now built for both AMD64 and ARM64 architectures (#7357).
Additionally, it is now much easier to build custom images by running make docker-build-dep from within the image’s folder.
We have also updated to the following package versions:
- Python 3.11.6
- JupyterLab 3.6.6
- Tensorflow 2.13.0 and CUDA 11.8 (for Tensoflow CUDA images)
- PyTorch 2.1.0 and CUDA 12.1 (for PyTorch CUDA images)
Platform dependencies
Kubeflow 1.8 includes hundreds of commits. The Kubeflow release process includes several rounds of testing by the Kubeflow working groups and Kubeflow distributions. Kubeflow’s configuration options provide a high degree of flexibility. After considering all of the testing options, the 1.8 Release Team narrowed the critical dependencies for consistent testing and documentation to the following.
| Component | Knative | Istio | Kubernetes | Cert-Manager | Kustomize | Dex | Argo | Tekton | Oidc |
| Version used in 1.8 | 1.10.2 (Serving) 1.10.1 (Eventing) | 1.17.3 | 1.25/1.26 | 1.12.2 | 5.0.3 | 2.36.0 | 3.3.10 | 0.47.5 | e236439 |
The 1.8 documentation includes overall installation instructions from the Manifest Working Group, and detailed feature reviews from each Kubeflow working group. Most of the working groups have broken their changelogs into subsections that highlight core features, UI enhancements, miscellaneous updates, bug fixes and breaking changes.
What’s next
The community continues to see a large increase in activity since the announcement that Kubeflow is now part of the CNCF Incubator. The community holds regular meetings and holds elections for the Kubeflow steering committee in the next few weeks.
During the 1.8 release cycle, the community continues to work in terms of security, issue triage and documentation. Our next releases will focus on helping build components for training LLMs and scalability.
How to get started with 1.8
For trying out Kubeflow 1.8 we recommend our installation page where you can choose between a selection of Kubeflow distributions. For more advanced users we also provide the manifest installation guide. We continue to test and improve the documentation. If you find an issue, please feel free to report and/or open a PR to help improve it for others.
Join the Community
We would like to thank everyone for their contribution to Kubeflow 1.8, especially Daniela Plasencia for his work as the v1.8 Release Manager. As you can see, the Kubeflow community is vibrant and diverse, solving real-world problems for organizations worldwide.
Want to help?
Want to help? The Kubeflow community Working Groups hold open meetings and are always looking for more volunteers and users to unlock the potential of machine learning. If you’re interested in becoming a Kubeflow contributor, please feel free to check out the resources below. We look forward to working with you!
- Visit our Kubeflow website or Kubeflow GitHub Page
- Join the Kubeflow Slack channel
- Join the kubeflow-discuss mailing list
- Attend a weekly community meeting